How to use relative file module with Create React app
Issue #751
Declare data/package.json to make it into node module
1 | { |
Then in landing/package.json, use file
1 | { |
Issue #751
Declare data/package.json to make it into node module
1 | { |
Then in landing/package.json, use file
1 | { |
Issue #700
In index.css
1 | body { |
Updated at 2020-11-18 06:29:29
Issue #699
Use term ZStack like in SwiftUI, we declare container as relative position. For now it uses only 2 items from props.children but can be tweaked to support mutiple
1 | class App extends React.Component { |
1 | /** @jsx jsx */ |
Updated at 2021-01-15 22:03:49
Issue #669
Specify params as array [year, id], not object {year, id}
1 | const { year, id } = props |
By default, it runs both after the first render and after every update.
This requirement is common enough that it is built into the useEffect Hook API. You can tell React to skip applying an effect if certain values haven’t changed between re-renders. To do so, pass an array as an optional second argument to useEffect:
1 | useEffect(() => { |
Updated at 2020-06-17 06:21:08
Issue #665
Usually in header we have logo that takes user back to the home page
1 | // index.js |
1 | // Header.js |
Issue #664
Use moment-timezone https://momentjs.com/timezone/docs/
1 | npm install moment-timezone |
Need to import from moment-timezone, not moment
1 | import moment from 'moment-timezone' |
Issue #663
1 | /** @jsx jsx */ |
Updated at 2020-06-17 05:38:30
Issue #662
Use spread operator
1 | import React, { Component, useState, useEffect } from 'react'; |
Updated at 2020-06-12 21:23:42
Issue #661
Use Bulma css
1 | <input |
Updated at 2020-06-16 07:30:52
Issue #661
Use Bulma css
1 | <input |
Issue #659
Use useLocation https://reacttraining.com/react-router/web/guides/scroll-restoration
1 | import React, { useEffect } from 'react'; |
Updated at 2020-06-04 05:58:47
Issue #658
Declare routes, use exact to match exact path as finding route is from top to bottom. For dynamic route, I find that we need to use render and pass the props manually.
Declare Router as the rooter with Header, Content and Footer. Inside Content there is the Switch, so header and footer stay the same across pages
1 | import { |
To trigger route request, use useHistory hook. Note that we need to declare variable, and not use useHistory().push directly
1 | import { useHistory } from 'react-router-dom' |
To get parameters, use match
1 | export default function BookDetail(props) { |
Updated at 2020-06-03 05:07:00
Issue #657
Add library folder src/library
1 | src |
Declare package.json in library folder
1 | { |
Declare library as dependency in root package.json
1 | "dependencies": { |
Now import like normal, for example in src/screens/Home/index.js
1 | import res from 'library/res' |
Issue #655
Declare state and setState
1 | export default function Showcase(props) { |
Issue #654
A good landing page is one of the most crucial part of a successful launch. Recently I started creating landing pages for my apps, I was lazy that I ended creating a white label React app as a landing template and then write a script to build multiple similar pages.
Here are a few examples, at first the pages share same look and feel, but we can add more configuration parameters later on. The cool thing with this approach is fixing bugs and adding features become easier, as they will all be deployed with the generator script.
Here are how it looks in my apps PastePal and PushHero, look at how the footer parts are so consistent.
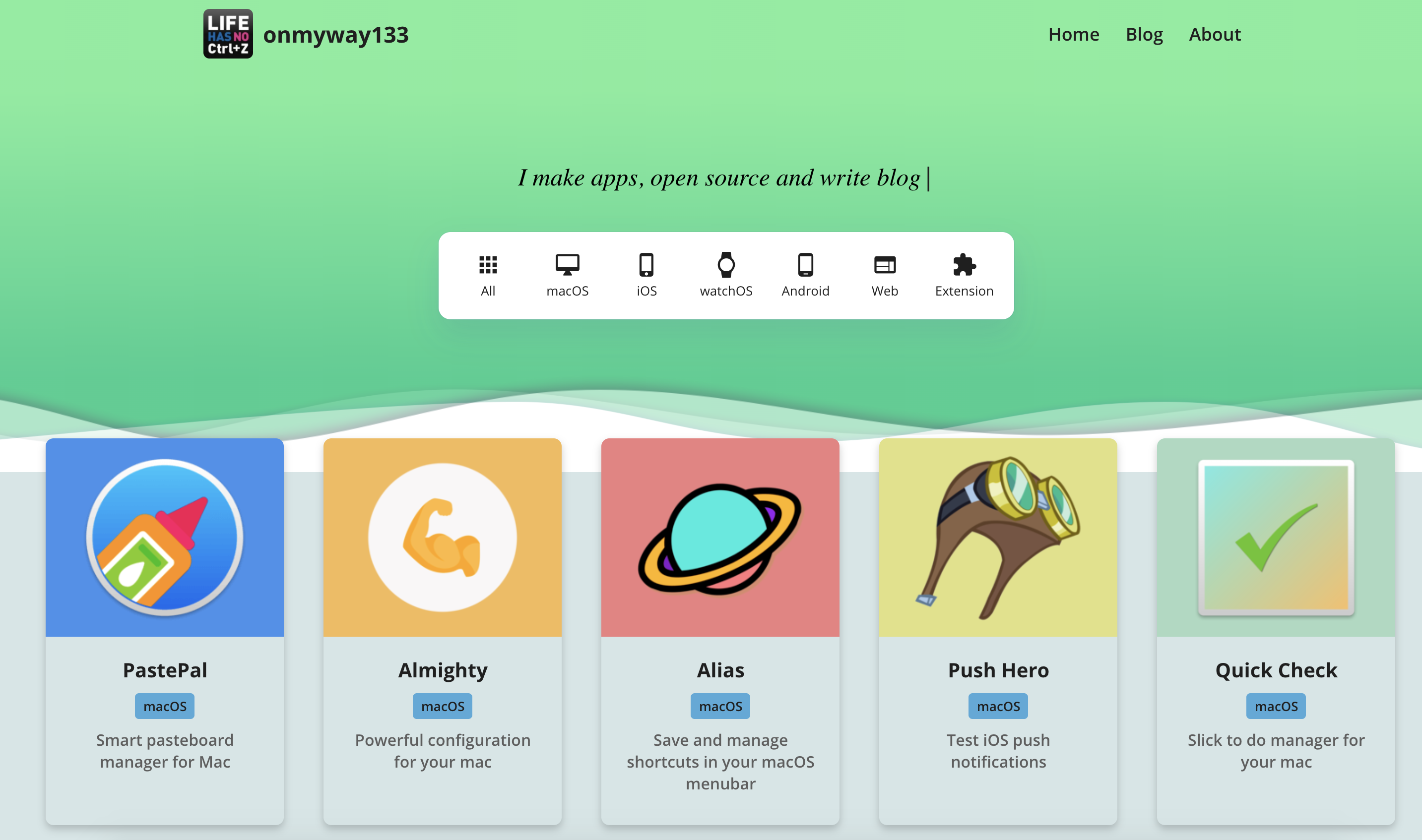
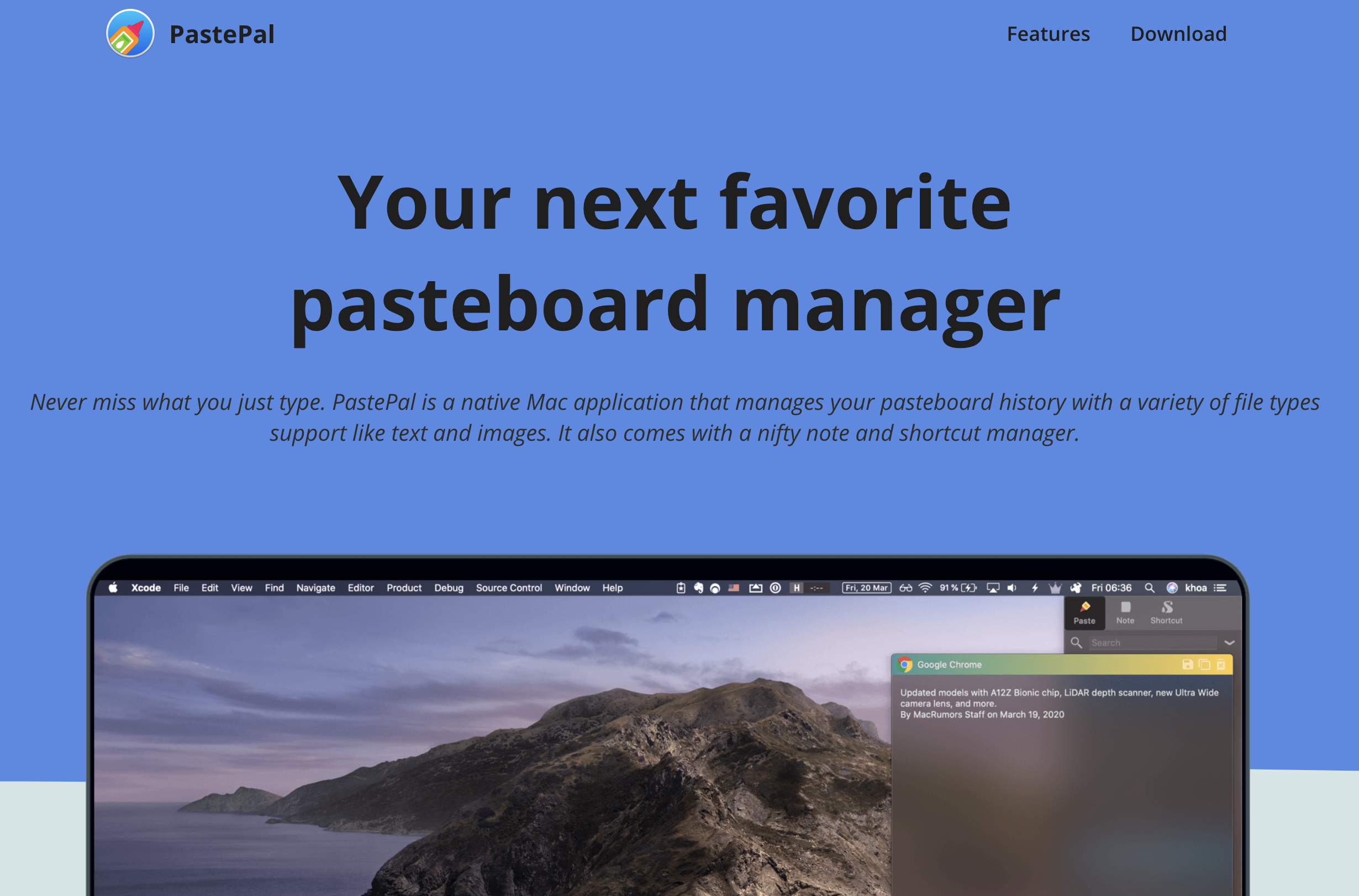
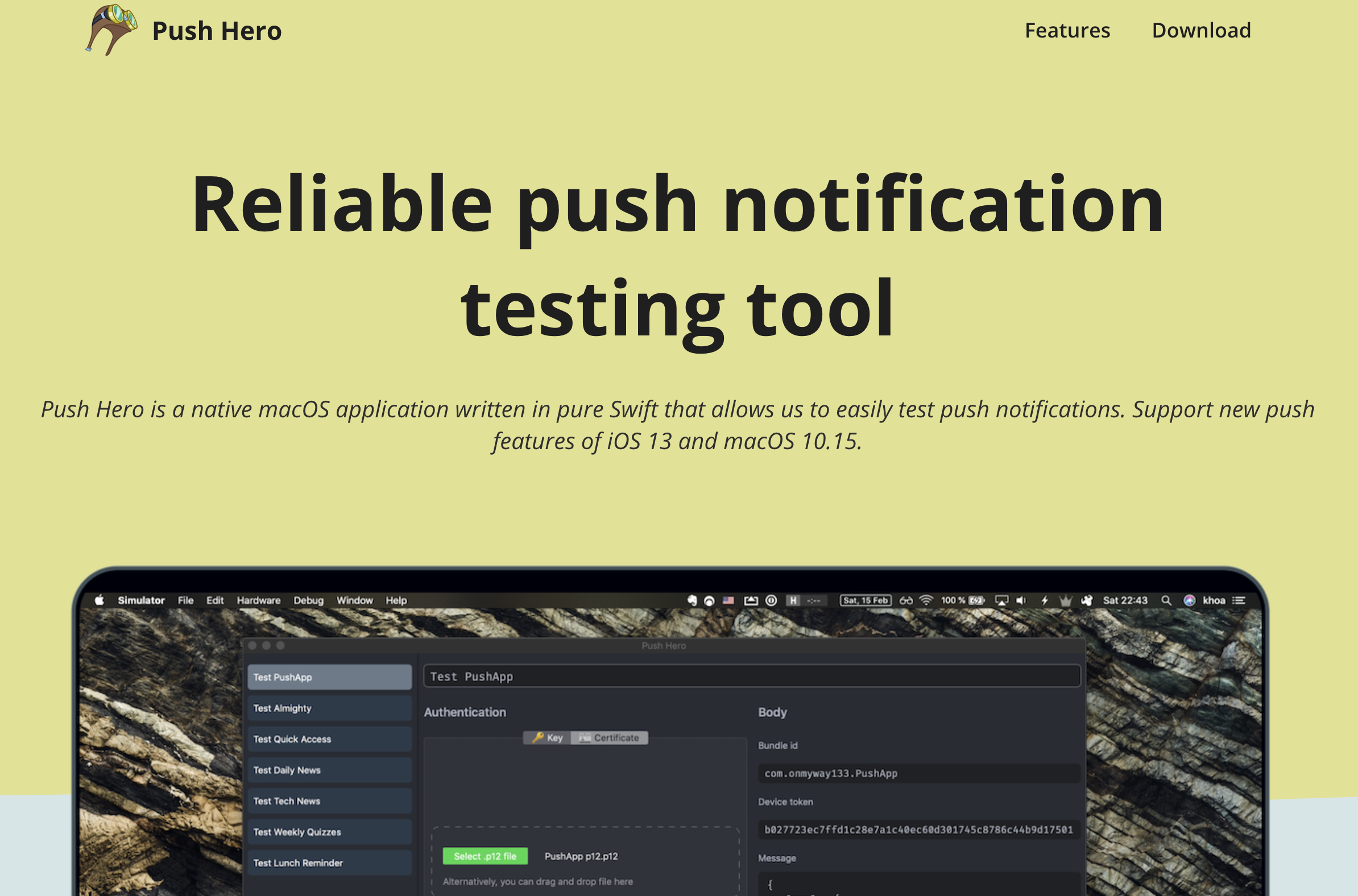
The first version that I built is with pure html and javascript. It has a lot of boilerplate and I need to deal with Webpack eventually to obfuscate my code.
1 | const cards = Array.from(apps).map((app) => { |
Since they are in pure html and javascript, everyone can just open browser and view source code, which is not ideal, so I need to fiddle with Webpack and other uglify and minimize tools to obfuscate the code, like How to use webpack to bundle html css js
1 | npm init |
And with external css sheets, finding and renaming class list names take some time.
I use create-react-app to generate my React app as it sets up JSX, Babel, Webpack, hot reloading and development server for me.
I like js, css and html be part of the same component file, so I prefer inline css. I tried styled-components before but then I found emotion to be much easier to use and close to css. I also don’t like declaring unnecessary local variables style in styled-components.
Here is a good comparison between the 2 styled-components-vs-emotion
1 | // styled-components |
1 | // emotion |
I detail here How to use emotion for inline css in React
Emotion has core and styled styles. I usually use the css inline syntax, so I can just install the core
1 | npm i @emotion/core |
Note that we have to declare jsx directive at the top of every file.
1 | // this comment tells babel to convert jsx to calls to a function called jsx instead of React.createElement |
One cool thing with inline css is they are just javascript code so it’s pretty easy to apply logic code, like in How to conditionally apply css in emotion js
1 | const shadowCss = feature.shadow ? css` |
When a component gets too big, I extract it to small components, in the end I have a bunch of them
1 | import Footer from './components/Footer' |
and I stack them vertically, using flexbox and css grid
I used flexbox mostly at first, but then I gradually convert some of them to css grid when I see fit. To stack vertically with flexbox, I use flex-direction
1 | display: flex; |
where as in css grid items are stacked vertically by default, if we want multiple columns, specify grid-template-columns
1 | display: grid; |
I use flex-wrap: wrap in some places to wrap content, but in some places I see specifying media query and changing columns in css grid is more easier and predictable
1 | display: grid; |
Google Lighthouse is the most popular tool to audit website for performance and SEO. I use it to reduce image size, add correct html attributes and make it more SEO friendly.
I have my list of apps in 1 javascript file, called factory.js, for example here with PastePal
1 | const factory = [ |
In my package.json for my landing page, I declare a property called currentApp. This is to specify which app I’m currently work on. Later in the generator script, we can just update this for every app that we build.
1 | { |
Here is how to read that value from my landing app
1 | import factory from './apps/factory' |
One thing with create-react-app is that built assets are relative to the root, not your index.html
npm run build creates a build directory with a production build of your app. Set up your favorite HTTP server so that a visitor to your site is served index.html, and requests to static paths like /static/js/main.
.js are served with the contents of the /static/js/main. .js file. For more information see the production build section.
If you are not using the HTML5 pushState history API or not using client-side routing at all, it is unnecessary to specify the URL from which your app will be served. Instead, you can put this in your package.json:
1 | "homepage": ".", |
This will make sure that all the asset paths are relative to index.html. You will then be able to move your app from http://mywebsite.com to http://mywebsite.com/relativepath or even http://mywebsite.com/relative/path without having to rebuild it.
I make another nodejs project called generator, it will use my landing project as template, changes a few parameters and build each app defined in factory.js.
My factory use export default syntax, so I need to use Babel in my node app to import that, see How to use babel 7 in node project
1 | npm init generator |
1 | { |
I use sync methods of fs to not have to deal with asynchrony.
1 | const pkPath = `/Users/khoa/projects/anding/package.json` |
I use shelljs to execute shell commands, and fs to read and write. In public/index.html specify some placeholder and we will replace those in our script.
In landing app, the public/index.html acts as the shell when building the app, so I have a few placeholder called CONSTANTS, these will be replaced at generation time in my node app.
1 | const fs = require('fs'); |
Updated at 2020-05-14 04:25:39
Issue #654
Use shelljs to execute shell commands, and fs to read and write. In public/index.html specify some placeholder and we will replace those in our script
1 | const fs = require('fs'); |
Issue #653
Use https://github.com/biati-digital/glightbox
Configure css. Specify class='glightbox for html elements
1 | <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/blueimp-gallery.min.css" /> |
Install package
1 | npm install glightbox |
1 | const lbElements = features.map((feature) => { |
Issue #652
Use https://github.com/michalsnik/aos
Add link to head
1 | <head> |
Jus before closing body tag
1 | <script src="https://unpkg.com/aos@next/dist/aos.js"></script> |
Specify data-aos
1 | <div data-aos="fade-up"> |
Issue #649
Check flag then define css
1 | const Picture = (feature) => { |
Issue #648
In a similar fashion to plain old javascript, note that href needs to have valid hash tag, like #features
1 | <a |
Updated at 2020-05-06 08:36:21
Issue #647
emotion can be used in framework agnostic or with React. To use with React, follow https://emotion.sh/docs/introduction#react
1 | npm i @emotion/core |
Note that you must have /** @jsx jsx */ at the top of the file, and the unused jsx in import is a directive for JSX to work properly
1 | // this comment tells babel to convert jsx to calls to a function called jsx instead of React.createElement |
Issue #352
For a normal electron app created with npm init, we can use all features of ES6, but not the JSX syntax for React. We can use just Babel to transpile JSX, as used in IconGenerator
.babelrc
1 | { |
And in package.json, call babel to transpile src to dist
1 | "main": "dist/main.js", |
Remember to use dist/main.js as our starting point, and in index.html, specify ./dist/renderer.js
1 | <body> |
Issue #192
Read https://www.apollographql.com/docs/react/features/error-handling
How to catch actual error https://github.com/apollographql/apollo-client/issues/4016 🤔
1 | import { Observable } from 'apollo-link' |
Issue #190
1 | render() { |